Intestinal epithelial barrier regulation and Crohn’s disease
Members
Daniela Kugelmann
Evelyn Ploner
Sabine Mühlsimer (technician)
Kang da Eun (MD student)
This is a project funded via the DFG SPP “Epithelial intercellular junctions as dynamic signaling hubs to integrate forces, signals and cell behavior” in which we study the mechanisms underlying intestinal barrier regulation by desmosomal contacts and their role in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease together with the group of Nicolas Schlegel at the surgery department of the university of Würzburg (http://www.zom-wuerzburg.de/index.php?id=423).
Crohn’s disease (CD) is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) with complex pathogenesis which is characterized by impaired intestinal epithelial barrier integrity. We previously showed that desmosomes are required for maintenance of barrier properties in enterocytes and that desmoglein 2 (Dsg2), which together with desmocollin 2 is the major desmosomal adhesion molecule, is crucial in this context (Figure 1).
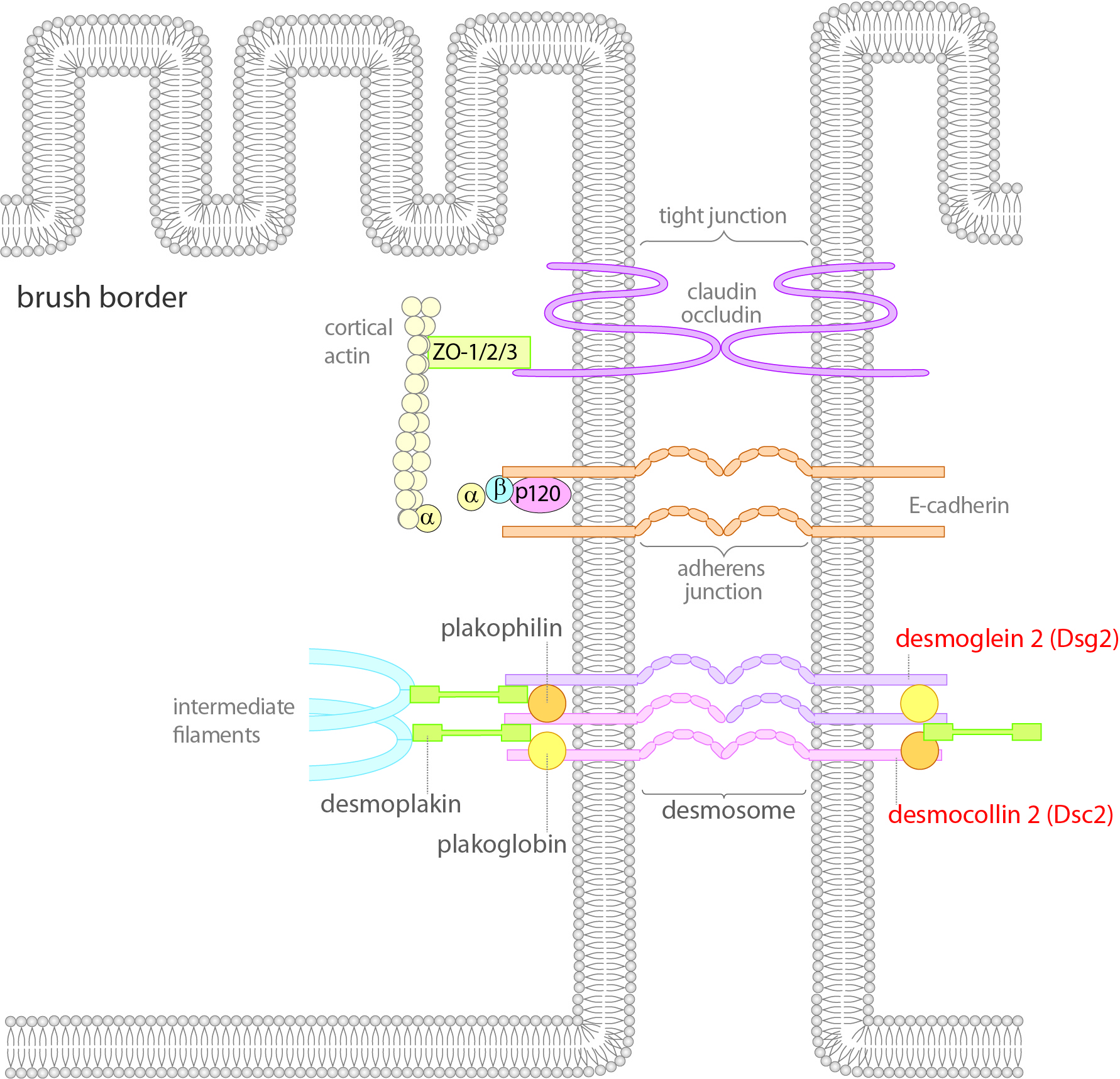
Figure 1
Therefore, we started to investigate the role of Dsg2 in CD and found that in patients’ intestinal biopsies suffering from conservative refractory CD Dsg2 is reduced and displays altered localization. Our data indicate that tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), which is well known to be involved in CD pathogenesis compromised Dsg2-dependent enterocyte cohesion at least in part via p38MAPK (Figure 2). Since a Dsg-specific tandem-peptide can block the negative effects of TNFα on the intestinal barrier, we assume that signaling pathways downstream of Dsg2 regulate tight junction integrity.
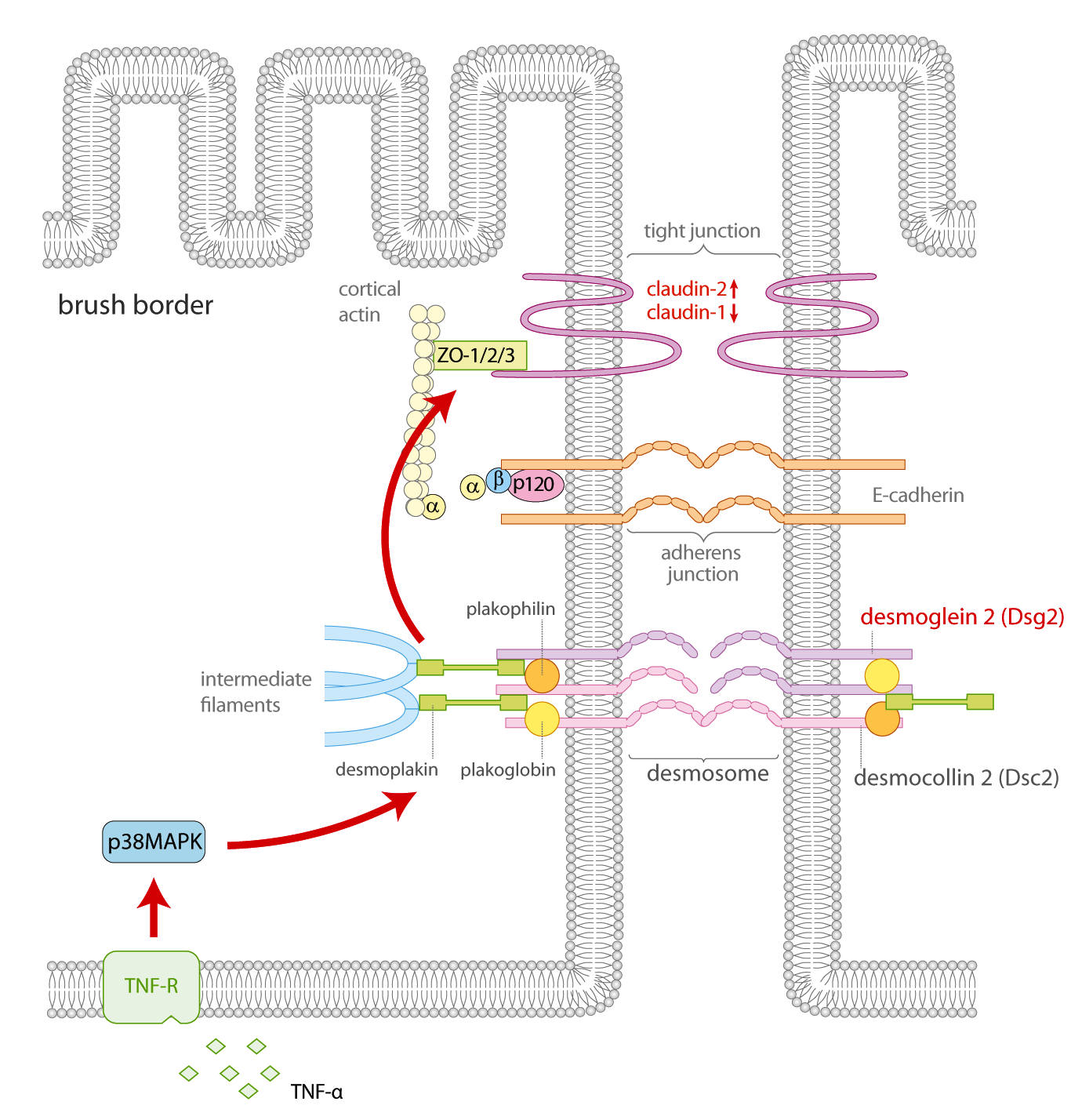
Figure 2
Publications
Hoelz H, Faro T, Frank ML, Forné I, Kugelmann D, Jurk A, Buehler S, Siebert K, Matchado M, Straub T, Hering A, Piontek G, Mueller S, Koletzko S, List M, Steiger K, Rudelius M, Waschke J, Schwerd T (2025)
Persistent desmoglein-1 downregulation and periostin accumulation in histologic remission of eosinophilic esophagitis.
J Allergy Clin Immunol.: S0091-6749(24)00990-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2024.09.016.
Nagler S, Ghoreishi Y, Kollmann C, Kelm M, Gerull B, Waschke J, Burkard N, Schlegel N (2022)
Plakophilin 2 regulates intestinal barrier function by modulating protein kinase C activity in vitro.
Tissue Barriers.;11(4):2138061. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2022.2138061.
Fuchs M, Kugelmann D, Schlegel N, Vielmuth F, Waschke J (2022)
Desmoglein 2 can undergo Ca2+-dependent interactions with both desmosomal and classical cadherins including E-cadherin and N-cadherin.
Biophys J. 121(7):1322-1335.
Burkard N, Meir M, Kannapin F, Otto C, Petzke M, Germer CT, Waschke J, Schlegel N (2021)
Desmoglein2 Regulates Claudin2 Expression by Sequestering PI-3-Kinase in Intestinal Epithelial Cells.
Front Immunol. 12:756321.
Meir M, Kannapin F, Diefenbacher M, Ghoreishi Y, Kollmann C, Flemming S, Germer CT, Waschke J, Leven P, Schneider R, Wehner S, Burkard N, Schlegel N (2021)
Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Maturation by Enteric Glial Cells Is GDNF-Dependent.
Int J Mol Sci 22(4):1887.
Meir M, Salm J, Fey C, Schweinlin M, Kollmann C, Kannapin F, Germer CT, Waschke J, Beck C, Burkard N, Metzger M, Schlegel N (2020)
Enteroids generated from patients with severe inflammation in Crohn's disease maintain alterations of junctional proteins.
J. Crohns and Colitis, 14(10):1473-1487.
Schlegel N, Boerner K, Waschke J (2020)
Targeting desmosomal adhesion and signalling for intestinal barrier stabilization in inflammatory bowel diseases-Lessons from experimental models and patients.
Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2020 May 18:e13492. doi: 10.1111/apha.13492. Online ahead of print. PMID: 32419327 Review.
Meir M, Burkard N, Ungewiß H, Diefenbacher M, Flemming S, Kannapin F, Germer CT, Schweinlin M, Metzger M, Waschke J, Schlegel N (2019)
Neurotrophic factor GDNF regulates intestinal barrier function in inflammatory bowel disease.
J Clin Invest. 2019 Jun 17;129(7):2824-2840. doi: 10.1172/JCI120261. eCollection 2019 Jun 17. PMID: 31205031 Free PMC article.
Gross A, Pack LAP, Schacht GM, Kant S, Ungewiss H, Meir M, Schlegel N, Preisinger C, Boor P, Guldiken N, Krusche CA, Sellge G, Trautwein C, Waschke J, Heuser A, Leube RE, Strnad P (2018)
Desmoglein 2, but not desmocollin 2, protects intestinal epithelia from injury.
Mucosal Immunol. 2018 Nov;11(6):1630-1639. doi: 10.1038/s41385-018-0062-z. Epub 2018 Aug 16. PMID: 30115995
Ungewiß H, Rötzer V, Meir M, Fey C, Diefenbacher M, Schlegel N, Waschke J (2018)
Dsg2 via Src-mediated transactivation shapes EGFR signaling towards cell adhesion.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 Nov;75(22):4251-4268. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2869-x. Epub 2018 Jul 6
Ungewiß H, Vielmuth F, Suzuki ST, Maiser A, Harz H, Leonhardt H, Kugelmann D, Schlegel N, Waschke J (2017)
Desmoglein 2 regulates the intestinal epithelial barrier via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase.
Sci Rep., 7(1):6329.
Spindler V, Meir M, Vigh B, Flemming S, Hütz K, Germer CT, Waschke J, Schlegel N (2015)
Loss of desmoglein2 contributes to the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease.
Inflamm Bowel Dis, 21(10):2349-59
Schlegel N, Meir M., Heupel WM, Holthöfer B, Leube R, Waschke J (2010)
Desmoglein 2-mediated adhesion is required for intestinal epithelial barrier integrity.
AJP Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology ,298(5):774-783

